Table of Contents
Revised on March 20, 2023
Non-genetically modified organisms are referred to as non-GMO, while GMOs (genetically modified organisms) are organisms that have been genetically changed or engineered in a laboratory.
What is a GMO (Genetically Modified Organism)?
Plants, animals, microbes, and other elements that have been altered by scientists to accelerate growth, production, or usage as food are known as GMOs. These effects are achieved by altering or modifying genes in ways that were not originally feasible (cross-breeding/hybridization).
GMOs carry dietary dangers that many consumers are reluctant to accept. This anxiety derives from the fact that there has been so little research on the dangers of GMOs to health and how they pollute the planet. One particular cause of uncertainty is the risk that GMOs will harm human health. This could be due to dietary changes, allergic reactions, or unfavorable side effects like toxicity, organ failure, or genetic alteration.
Businesses respond to these claims by claiming that they are developing goods that have greater returns, are easier to handle, and require lesser resources and energy consumption. They claim that these advantages far exceed the concerns raised by anti-GMO protests.
The GMO Controversy— What are the dangers of genetically modified organisms (GMOs)?
Items that have been genetically modified have sparked debate over the years. In most cases, genetic engineering alters an organism in unnatural ways. The mixing of genes is a common practice in GMO processing, increasing the chance of unanticipated allergy reactions to certain GMO foods. Further risks involve the danger of foreign DNA from genetically modified plants and animals transferring to non-GMO plants and animals.
The Non-GMO Project divides GMO products into four risk categories, including high-risk, low risk, non-risk, and monitored risk.
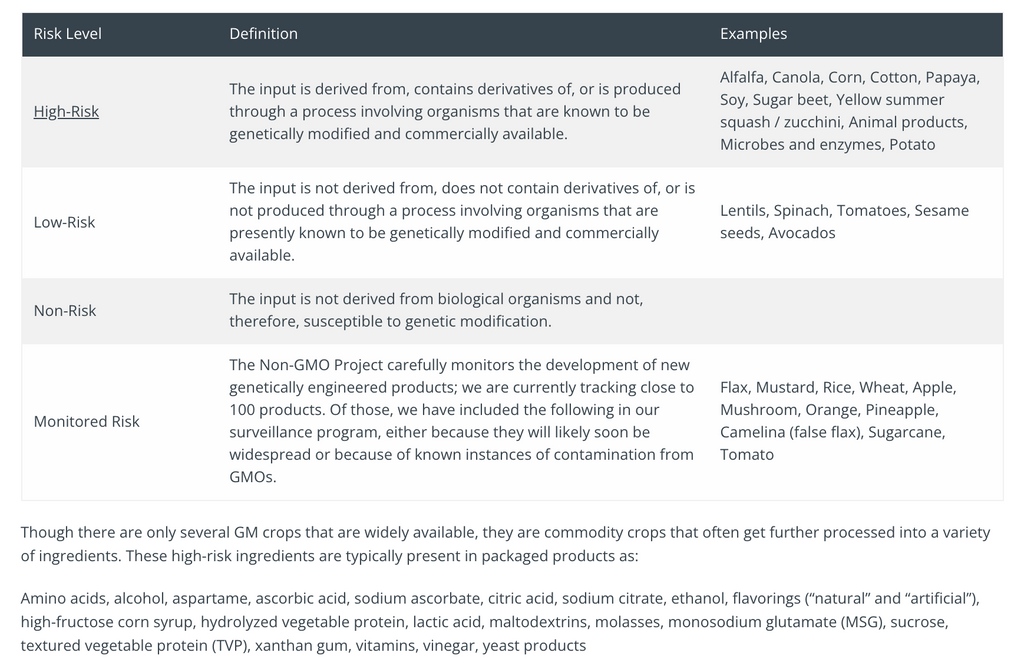
Image Credit: Non-GMO Project
What Does It Mean To Be GMO-Free or Non-GMO?
An item labeled as Non-GMO indicates that the ingredients used for manufacturing the product were produced without any laboratory modification. It refers to food that does not contain substances obtained from genetically modified organisms. For example, non-GMO poultry, meat, or dairy come from animals that have not been raised with genetically modified crops.
Then again, the label claim on its own isn't necessarily reliable because it isn't always validated by a third party. To be sure, check for a verified non-GMO label such as the Non-GMO Project Verified seal or the USDA Organic seal.
What is a Non-GMO Project?

The Non-GMO Project is a non-profit organization that offers a third-party labeling program for products developed without the use of genetic engineering. They ensure that the entire manufacturing process is carried out per their strict GMO-free standards.
The Organic Possibility— Alternative Labels To Non-GMO
The organic label is another option for anti-GMO campaigners. Instead of focusing just on GMOs, they should look for goods that bear the "Organic" label. Check for the following additional certified labels to ensure the absence of hazardous substances.

Image credit: Only Organic
How Do Farms Avoid Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)?
Complete avoidance of GMOs is becoming increasingly challenging given the widespread usage of genetically modified organisms in modern agriculture. Even farmers who desire to keep their fields GMO-free are finding it impossible due to unintentional exposure to farms that are dealing with GMO crops (spreading through wind and water).
Considering the complexity of the situation, the USDA has set a policy that even if GMOs are accidentally included in otherwise GMO-free crops, the product can still be certified organic. USDA also urges the use of planting methods that discourage accidentally mixing the GMOs and non-GMOs. These methods include rotating planting times, agreements with neighboring farms to avoid the use of GMOs, and the thorough cleaning of farm equipment used in processing both GMO and non-GMO crops.
Is Organic Cotton Non-GMO?
Organic cotton is a natural fiber grown with non-GMO seeds. To be more precise, it is non-toxic cotton grown without the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers. The farming practices entail organic agricultural methods that improve soil health, boost biodiversity, and lessen the water impact of fiber. These attributes make organic cotton material a chemical-free textile, a far better variant than conventionally grown cotton.
Terra Thread's organic cotton backpacks are free of harmful chemicals
The framing and production of organic cotton, an eco-friendly fabric, benefit the land, the farmers, and their communities. The prohibition of toxic chemicals and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) protect soil fertility and the welfare of the environment and people.
Conclusion
Labels only cover a portion of a farm's output. Non-GMO is not an assurance of pesticide-free or that a farm's soil was managed properly. Consider labels that are relevant to the items before making a purchase.






